Double Entry
System of Accounting
Double entry system of accounting is based on the dual
aspect concept. It includes two aspects, they are Debit aspects and Credit
aspects.
Debit Aspects- This includes either Receiving aspects,
incoming aspects or Expenditure aspects, these are known as Debit aspects.
Credit Aspects- The another aspects may be Giving aspects,
outgoing aspects or income aspects. These are known as Credit aspects.

Stages of Double Entry System
There are three distinct stages are includes a complete
system of double entry.
i)
Recording of transactions in the journal.
ii)
Posting of journal entry in to the respective
ledger accounts and then preparing a trial balance.
iii)
Closing of books of accounts and preparing final
accounts.
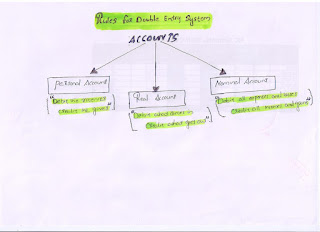
Rules for Double Entry System
An account is statement and it is a record of transactions
relating to a person, or a firm, or a property, or a liability, or an income or
expenditure. There are three kinds of rules for double entry system. They are
as follows:-
1.
Personal Accounts
Under this statement, a separate account will
be prepared for each person. It includes Natural peron’s account, Artificial
person’s account and representative personal accounts. Some of the examples of
personal account are Ramu’s account, Bank account, Any firms account, any
companies account, prepaid expense account, outstanding wages account etc.
Rule for personal Account:-
“Debit
the receiver
Credit the giver”
2.
Real Accounts
Under the real account, a separate account
will create for each class of property or asset. There will have an account
relating to a property, an asset or a possession of property. Some of the
examples for real account are Cash account, Furniture account, Goodwill account
etc.
Rule for Real Account:-
“Debit
what comes in
Credit what goes out”
3.
Nominal Account
These includes the expenses and losses or
incomes and gains of business. Some of the examples of Nominal account are
wages account, discount received account, interest account etc.
Rule for Real Account:-
“Debit
all expenses and losses
Credit all incomes and gains”
Advantages
of Double entry system
The important merits of Double entry system
are as follows:-
1.
Under Double entry system, keeps a complete
record of business transactions.
2.
This provides complete information regarding the
business.
3.
This has the facility of checking mathematical
accuracy of books of accounts.
4.
It reveals the profit or loss of the business
for a given period.
5.
This enables the business man to plan, control
and take necessary actions in his operations.
6.
It avoids chances of fraud or misappropriation
of accounts.
7.
This system is flexible according to the nature
of business.
8.
This system is accepted by the tax authorities.
9.
Actual net profit can be calculated directly.
Disadvantages
of Double entry system
The important limitations of Double entry
system are as follows:-
1.
It is not suitable to disclose all the
information of a transaction which is not properly recorded in the journal.
2.
If there is any errors in the transactions
recorded in the books, it is difficult to detecting the errors.
3.
This system required more clerical labour.
4.
If there is any compensatory errors, it is not
suitable to find out by this system.
These all are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Double
entry system of accounting.




